Fabric Printing Methods
Understanding How Your Fabric Is Printed and Why It Matters
Written Exclusively for Little Cocalico by Michael Sanders (Digital Bias Textile Consulting)
Printing patterns on fabric is an old art form, dating back many centuries. The oldest evidence we have of textile pattern printing dates back to China around 220 AD or earlier, where carved wood blocks were used to stamp patterns onto fabric. If we fast-forward to the 12th century, we have records of textile printing entering Europe via the Islamic world with the use of dyes applied via stencils or stamps.
Needless to say, fabric printing technology has changed significantly since that time. Today most of the global fabric production for apparel and home decor is done on flatbed and rotary screen printers, utilizing technologies that allow for printing large amounts of yardage at a time. While this method allows for mass-scale printing, it has its disadvantages and problems as well. In recent years various methods of digital fabric printing have risen as alternative printing methods. Digital printing removes the limitations of screen and rotary printing with yardage minimums and the number of colors available. This enables the apparel, home decor and signage industries to be served on a much smaller and custom scale.
In this article we will define and discuss the pros and cons of the most popular types of textile printing being used today, including the different methods of digital printing. We’ll also discuss why method matters and why digital pigment printing is the future of fabric printing and more sustainable and better for the environment.
What are the Different Methods of Fabric Printing?
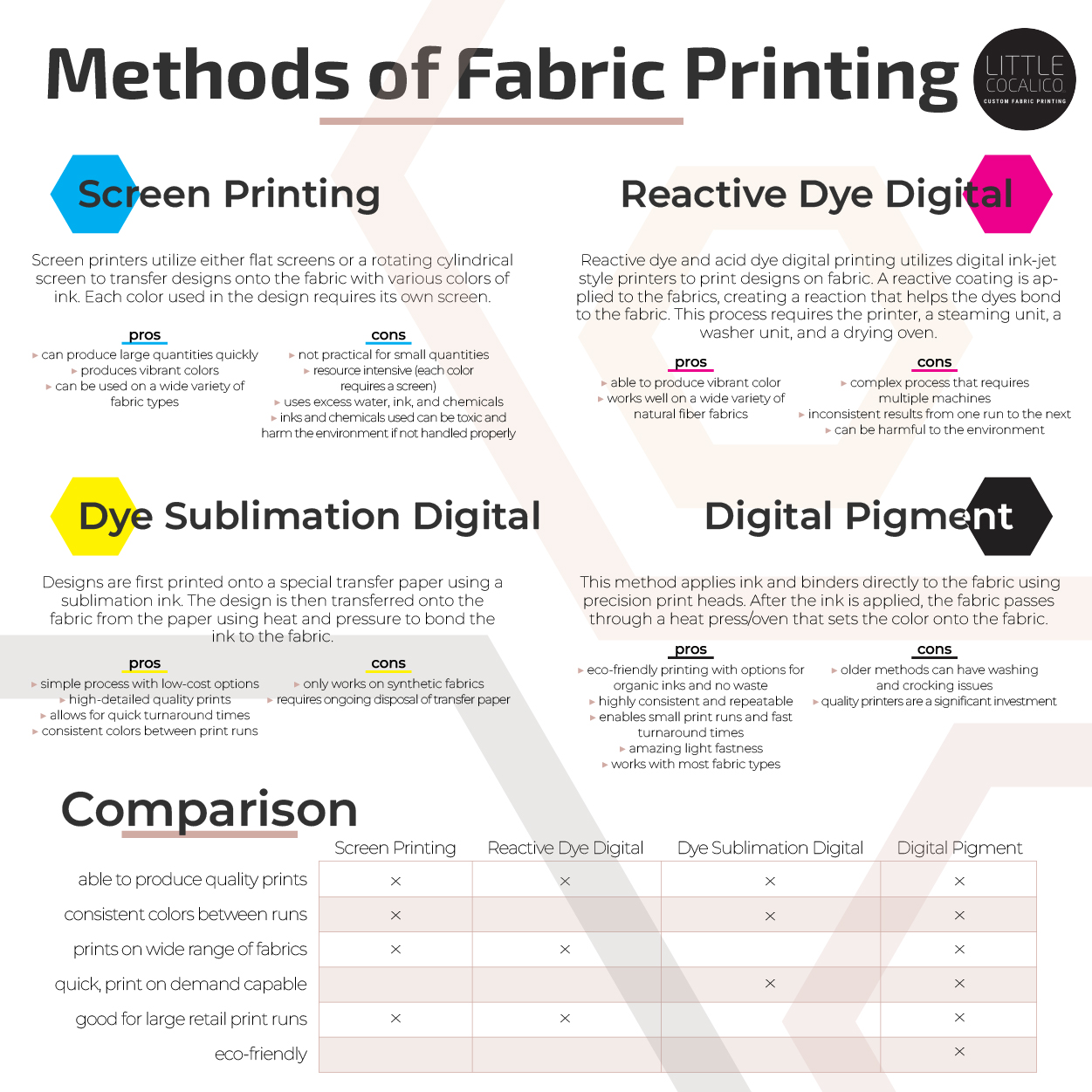
Screen Printing (Flatbed and Rotary)
As mentioned, much of the world’s fabric printing production has traditionally been done on flatbed or rotary screen printers. If you’ve purchased fabrics at large retail stores it’s likely that the fabric was printed overseas on a screen printer. Screen printers utilize either flat screens or a rotating cylindrical screen to essentially transfer the patterns onto the fabric with various colors of ink. Each color used in the design requires its own screen.
There are various types of inks and technologies used in screen printing. Water-Based Pigment printing is the most popular type because it works on all types of fabrics and blends while also being a more eco-friendly and repeatable process. Other processes utilize reactive dye printing for cotton and cellulosic fabrics, disperse printing for polyesters, and acid printing for nylons and silks.
Video of Flatbed Screen Printing
It’s important to remember that screen printing of fabric yardage is only good for large scale production due to the complexity and time of machine setup and the cost of screens and strike-offs. Most times any print run under 1,000 yards is considered a sample run and will include sample charges and setup costs. Screen costs for every color used in printing can vary from $300 per screen on a flatbed printer to $400 per screen for a rotary printer. More advanced screens, like Galvano screens, that produce higher detail and photo quality printing will cost over $1,000 per screen per color.
Pros of Screen Printing:
- Screen printing, particularly rotary printing, is a fast printing method that can produce large quantities of fabric quickly and efficiently.
- Able to produce vibrant colors
- Works on a wide variety of fabrics
- If over 1,000 yards, screen printing may be the better option.
Cons of Screen Printing
- Not practical for small scale printing and small business production
- Resource intensive, requiring creation of screens for every color used in every pattern.
- Ecologically wasteful and harmful. The traditional Flatbed and Rotary printers have a sticky belt that the fabric adheres to on the printer and it is continuously being washed. The excess water, inks, and chemicals are flowing into our sewers and oceans.
- Most of the ink and chemicals used in off-shore screen printing are unhealthy both for humans who come in contact with them and for the local environments that are impacted by the water runoff.
- Long turn-around-times on orders
So that’s the scoop on traditional screen printing. However, with the rise of digital printing methods all the traditional rules have changed. Let’s discuss the primary methods of digital printing being used today
Reactive Dye Digital Fabric Printing
Reactive dye and acid dye digital printing utilizes digital ink-jet style printers to print designs on fabric. A reactive coating is applied to the fabrics, creating a reaction that helps the reactive or acid dyes bond to the fabric. This process requires the printer, a steaming unit, a washer unit, and a drying oven. Through the process of steaming, washing, and drying a chemical reaction between the coating and the dye creates a long-lasting bond with the fabric.
Reactive dyes work well on all cellulose fibers such as cotton, linen, rayon, hemp, bamboo, and many other natural fiber fabrics. Acid dyes tend to work best on protein fibers like silk, wool, and nylon.
To use the reactive method of printing, a printer will need permits from AQMD (Air Quality Management Department) because the process discharges dyes and chemicals into the sewer through the washing process. Due to its complexity, reactive dye printing requires a good knowledge of the process and an awareness of its limitations.
One of these limitations is that this method is not completely repeatable due to the nature of the process. Since it relies on natural fibers that can change from batch to batch to print and create the bond, you will likely see small color changes from one print run to the next with the same design. For this reason, reactive dye printing is best for one-off printing runs.
Pros of Reactive Dye Printing:
- Able to produce vibrant color
- Works well on a wide variety of natural fiber fabrics
Cons of Reactive Dye Printing:
- Complex process that requires multiple machines
- Inconsistent results from one run to the next
- Can be environmentally harmful with water runoff into sewer system if not treated properly
Dye Sublimation Digital Fabric Printing
Dye sublimation fabric printing is a popular fabric printing method that has enabled many small print shops to open for custom fabric printing. It is not a direct to fabric printing method, but rather prints the design onto a special transfer paper using a sublimation ink. The design is then transferred onto the fabric from the paper using heat and pressure to bond the ink to the fabric. The heat and pressure causes the sublimation ink to transform into a gas and permeate the fibers of the fabric, creating a permanent, high-quality image.
While this is a very good printing method it does have its limitations and downsides. This process works only with synthetic fabrics like polyesters and will not work with natural fiber fabrics. Obviously these types of fabrics are not as green and healthy as natural fibers, causing many conscious shoppers to start steering away from synthetic fabric bases as more awareness has been raised in recent years. Dye sublimation also has some environmental concerns since it requires the ongoing usage and disposal of the transfer paper.
Pros of Dye Sublimation:
- Simple process with options for low-cost smaller printer setups to empower small businesses
- Quality, high-detail prints
- Digital process allows for quick turnaround time
- Repeatable process with consistent colors between print runs
Cons of Dye Sublimation:
- Only works on synthetic fabrics
- Requires ongoing disposal of transfer paper
Digital Pigment Fabric Printing
Pigment printing is fast becoming one the most popular methods of fabric printing. This is a versatile, printing method that applies pigments (fine particles of color) directly to the fabric using precision print heads. While pigment printing has always been considered an ideal in the industry, it has been difficult to get right. For years pigment printed fabrics were known to produce a stiff fabric, have limited color ranges, and have issues with crocking and wash-fastness. However, the scene has changed dramatically in recent years, thanks to a revolutionary patented printing technology from Kornit Digital.
Unlike other print methods, the Kornit method adds the binder through the printheads and also applies the softener at the same time. After the ink is applied, the fabric passes through a heat press/oven that sets the color onto the fabric. No pre-treatment of the fabric is required and no water used in the process, making this the most eco-friendly method of textile printing.
One of the factors that is making this method of pigment printing so popular, especially in the home furnishings industry, is the light fastness of the pigments. The new technology developments by companies like Kornit with binders, inks, and printheads are producing incredible results that eliminate any of the concerns with binders, stiffness, crocking, and color limitations.
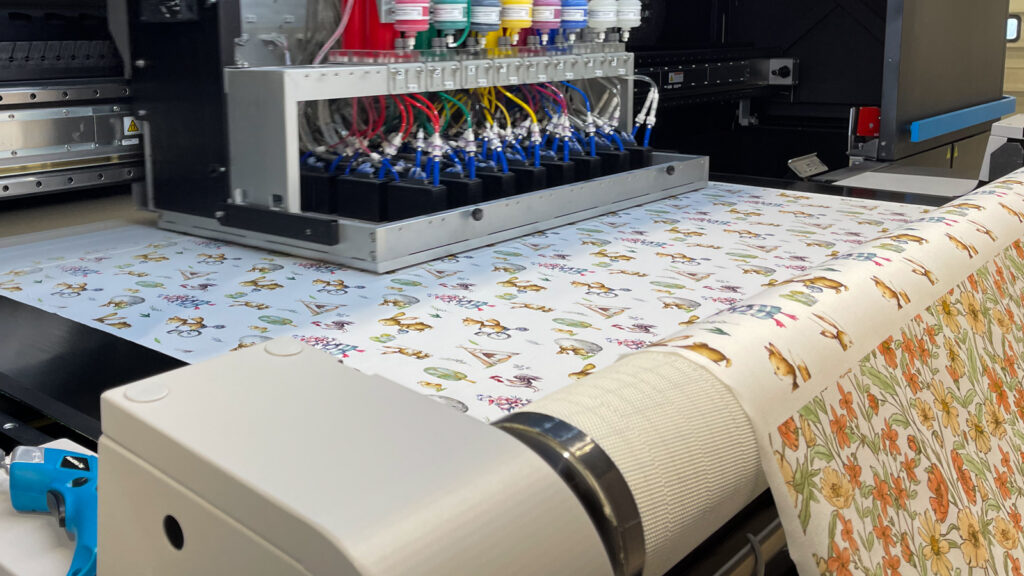


With pigments, the quality and durability of the print is all about the ink quality and the binder that is used to make the color adhere to the fabric. A poor-quality binder can create washing and crocking issues. Printer companies, like Kornit, have developed organic inks and binders that both produce some of the finest and most durable prints available while also being non-toxic and environmentally friendly.
Pigment printing can work very well with both natural fiber fabrics, synthetic fabrics, and fabrics blends. It is the most repeatable and consistent method of digital printing available today.
Pros of Pigment Printing:
- The most eco-friendly printing method with options for organic inks and no water or waste involved.
- Highly consistent and repeatable
- Enables small print runs and fast turnaround times
- Amazing light fastness
- Works on most fabric types
- Able to print photographic images without color range limitations
Cons of Pigment Printing:
- Old methods can have washing and crocking issues if poor binders are used (not an issue with Kornit printers)
- Quality printers are a significant investment
Fabric Printing Methods Infograph
Does Printing Method Matter?
After surveying the different printing methods that are commonly used, it is evident that there are significant differences and outcomes between the common printing methods. However, there is more at stake than just the quality of a print when it comes to textile printing. The textile production industry has large implications on the sustainability of the environment and economies around the world. Traditional methods of printing have been resource intensive and resulted in large amounts of contaminated waters flowing into waterways and sewers, harming the environment and the health of off-shore, local communities.
The types of inks used in the various textile printing methods can also have a large impact on global health. All over the world, humans are coming into contact with printed fabrics in many ways every day. From the clothes we wear, to furniture, to bedding – we are literally rubbing shoulders with printed fabrics. Ongoing research continues to show that fabric particle shedding is a legitimate health and environmental concern. With this in mind, the types of inks and chemicals used in the printing process definitely does matter.
One more way that the printing method matters is the impact it can have on supporting small businesses and local economies. Traditional methods of printing have not been as friendly toward the small business owner with the large order minimums and setup fees required. The development of printing methods that enable fast turnaround, no setup costs, and repeatable precision has made the textile industry much more friendly toward small businesses.
Textile printing method definitely matters!
Why Digital Pigment Printing is The Future of Fabric Printing
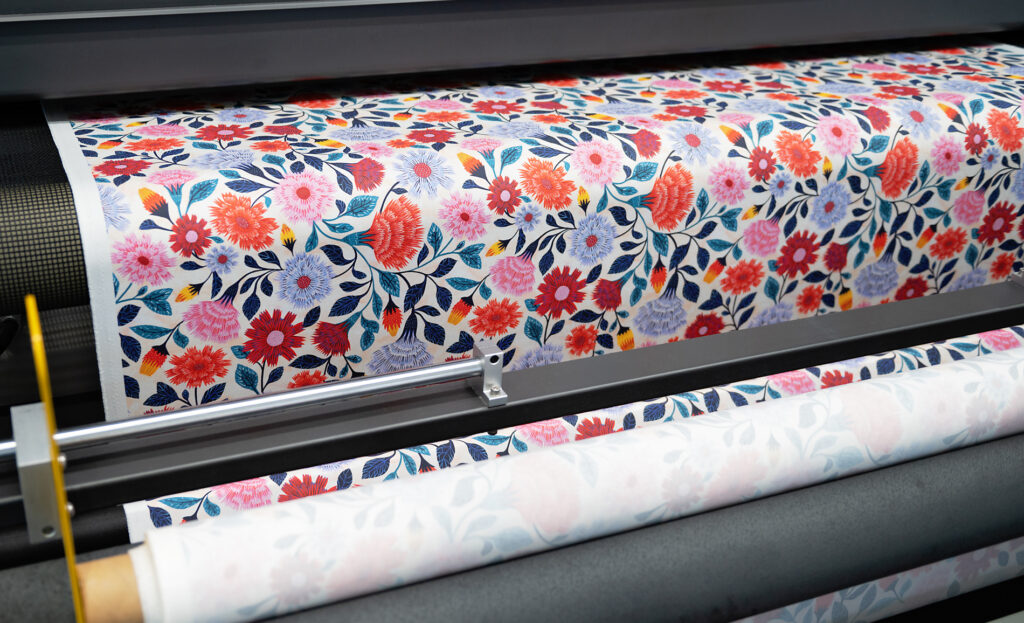

Over the last ten years, digital printing has evolved tremendously and continues to improve each year! There is no question that digital printing is the path forward in the textile industry. With digital printing there are no minimums with the amount of yardage being printed and the number of colors being used.
Digital printing has also drastically reduced the carbon footprint from the textile industry with cleaner printing processes and less waste.
However, as we saw above, there are still a variety of digital printing methods and some are better than others. Pigment printing has always been the golden fleece of Digital Printing. But, it has also been the hardest method to get right. The patented printing system that Kornit has developed in recent years is a game-changer for pigment printing. The ability to produce high quality prints using organic inks and binders with a system that doesn’t require any water or pre-treatment of the fabirc is a solution that is revolutionizing the textile world. And innovation isn’t finished yet. Better binders and softeners continue to be developed, improving the wash and rub durability of fabric prints and the hand of the fabric itself.
The technology will continue to evolve and improve, but I am confident that the future of textile printing is digital pigment printing. For consumers this is a great time to explore and use digitally printed fabrics for apparel and home decor. Fabric printers like Little Cocalico who use the Kornit Pigment printers are making eco-friendly custom fabrics readily available to the individual consumer, allowing you to customize the clothes you wear and the fabrics you use at home. It is exciting to live in an era that enables us to use beautiful and quality fabrics while changing the carbon footprint for the better. Supporting digital pigment printing will help to make our planet cleaner and greener while also enhancing your style and pallet. Enjoy your pigment printed fabrics!
Video of Digital Pigment Printing with Kornit Printer
About the Author

Michael Sanders is a textile craftsman with over 40 years of experience working in the textile industry. As an industry consultant he provides services to equipment manufacturers, print service providers, designers, and more. His areas of expertise involve all forms of digital printing, dyeing and finishing, textile development, textile team trainings, and other industry specific skills.
Website: digitalbiasconsulting.com
